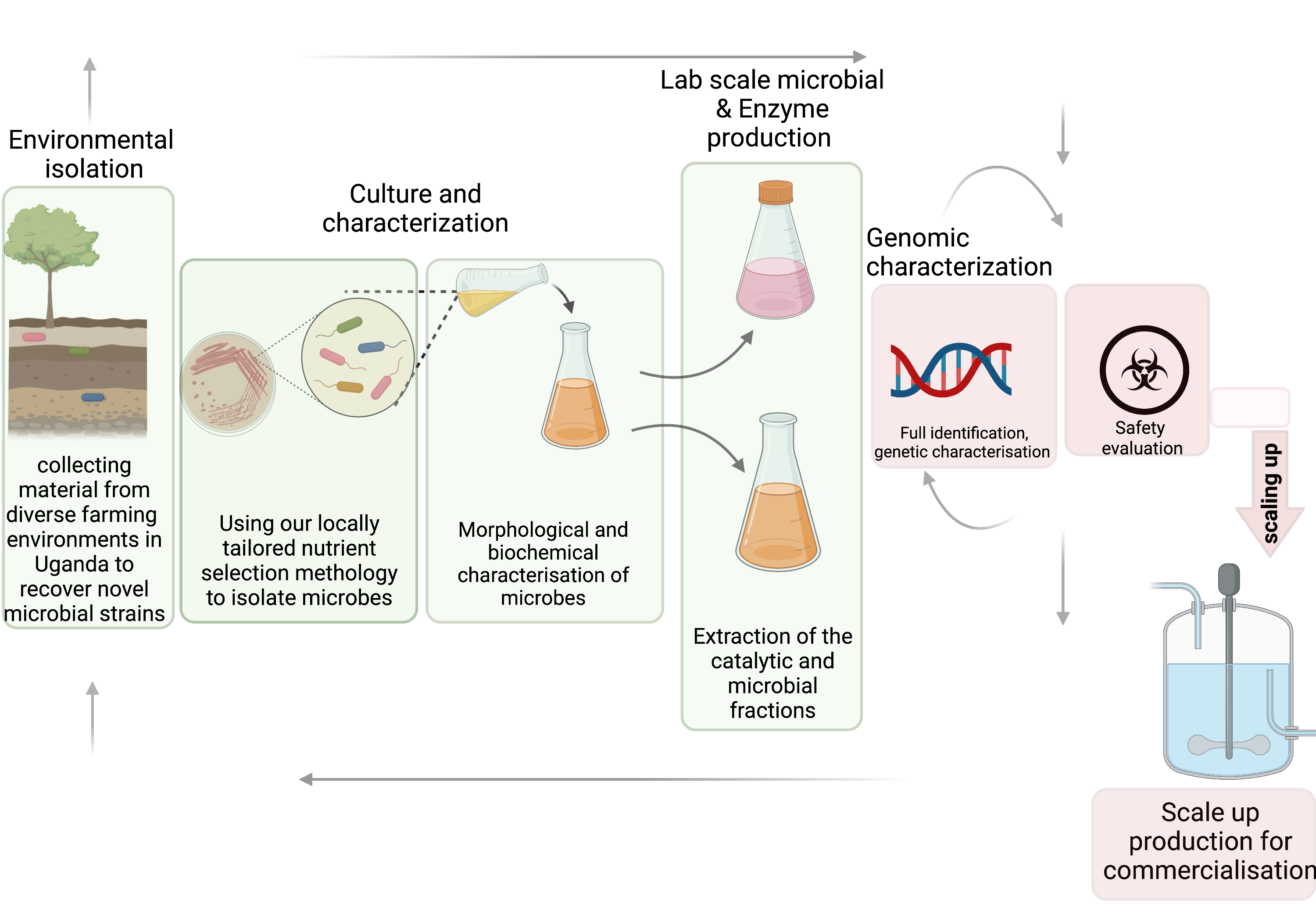
Discovery Process
We use a thorough five step processing in discovering unique microorganisms. We start by collecting samples from different farming environments in Uganda to find novel strains.
This is followed by culturing and characterization. We use novel growth media to isolate and select Bacillus and Aspergillus strains with specific characteristics